

What are Ice Phishing Attacks and How You Can Protect Yourself

Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, one term has been making waves, especially within the blockchain and cryptocurrency communities - "Ice Phishing." This sophisticated form of phishing attack has been on the rise, targeting individuals who use cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Understanding what ice phishing is and how to protect yourself is crucial in the world of web3. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of ice phishing attacks and provide essential tips on safeguarding your digital assets.

Unmasking Ice Phishing
Ice phishing, also known as phishing on the blockchain, is a type of scam designed to exploit users of cryptocurrency and blockchain platforms. Unlike traditional phishing, where attackers try to steal login credentials or personal information, ice phishing takes a more direct route to your digital assets.
The core objective of an ice phishing attack is to deceive users into approving a malicious transaction. Once signed, this allows the attacker to siphon off cryptocurrency tokens from the victim's wallet and transfer them to their own, effectively diverting the funds away from the rightful owner.
How Ice Phishing Works
To comprehend ice phishing fully, it's essential to grasp the mechanics of the attack. Here's a simplified overview of how an ice phishing attack typically unfolds:
- Deceptive Transaction: The attacker sends a transaction request to the victim, often masked as a seemingly harmless or legitimate interaction within a decentralized application (dApp) or smart contract.
- Approval Request: The victim is prompted to approve the transaction, usually under the guise of a routine action within the dApp. This request appears legitimate and may not raise immediate suspicion.
- Altered Transaction: Unbeknownst to the victim, the attacker has subtly altered the transaction details, such as the recipient's address. Instead of the intended destination, the funds are redirected to the attacker's wallet.
- Approval Granted: The victim signs off on the transaction, believing it to be safe. Once approved, the cryptocurrency tokens are transferred to the attacker's address.

A Notorious Example: The Badger DAO Attack
One of the most infamous ice phishing attacks in recent memory was the Badger DAO attack, which occurred in November-December 2021. Badger DAO is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that allows users to earn interest on Bitcoin deposits. With approximately $978 million in total value locked (TVL) at the time, it was a tempting target for attackers.
In this attack, the attacker compromised the Badger smart contract front-end infrastructure, gaining access to a Cloudflare API key. This breach allowed the attacker to inject a malicious script into the Badger smart contract front end. The script then prompted users to sign transactions that granted ERC-20 approvals to the attacker's account.
As a result of the attack, the attacker was able to drain approximately $121 million from nearly 200 accounts within a mere 10 hours. This incident underscored the urgent need for enhanced security measures in web3 environments.

Example of an Ice Phishing Attack
The initial phase of an ice phishing attack happens when the victim is deceived into granting approval for an EOA (Externally Owned Account) or a malicious smart contract to expend tokens from their wallet. An instance of this scenario is demonstrated in the transaction provided below:
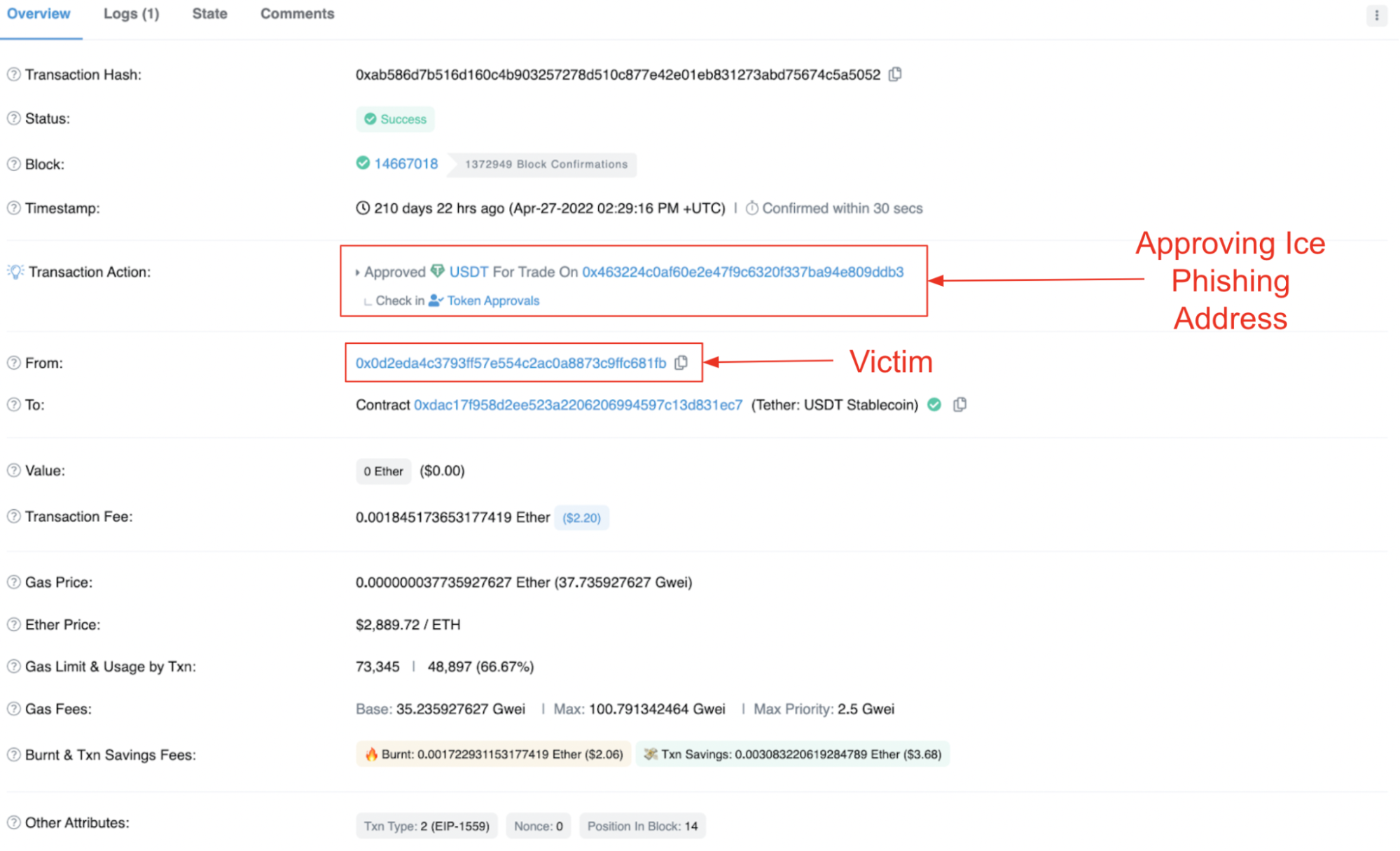
The second phase unfolds as the ice phishing address triggers a TransferFrom transaction, relocating tokens from the victim's account to an address designated by the ice phisher. In the example below, USDT tokens are transferred to the address 0x9ca3b...
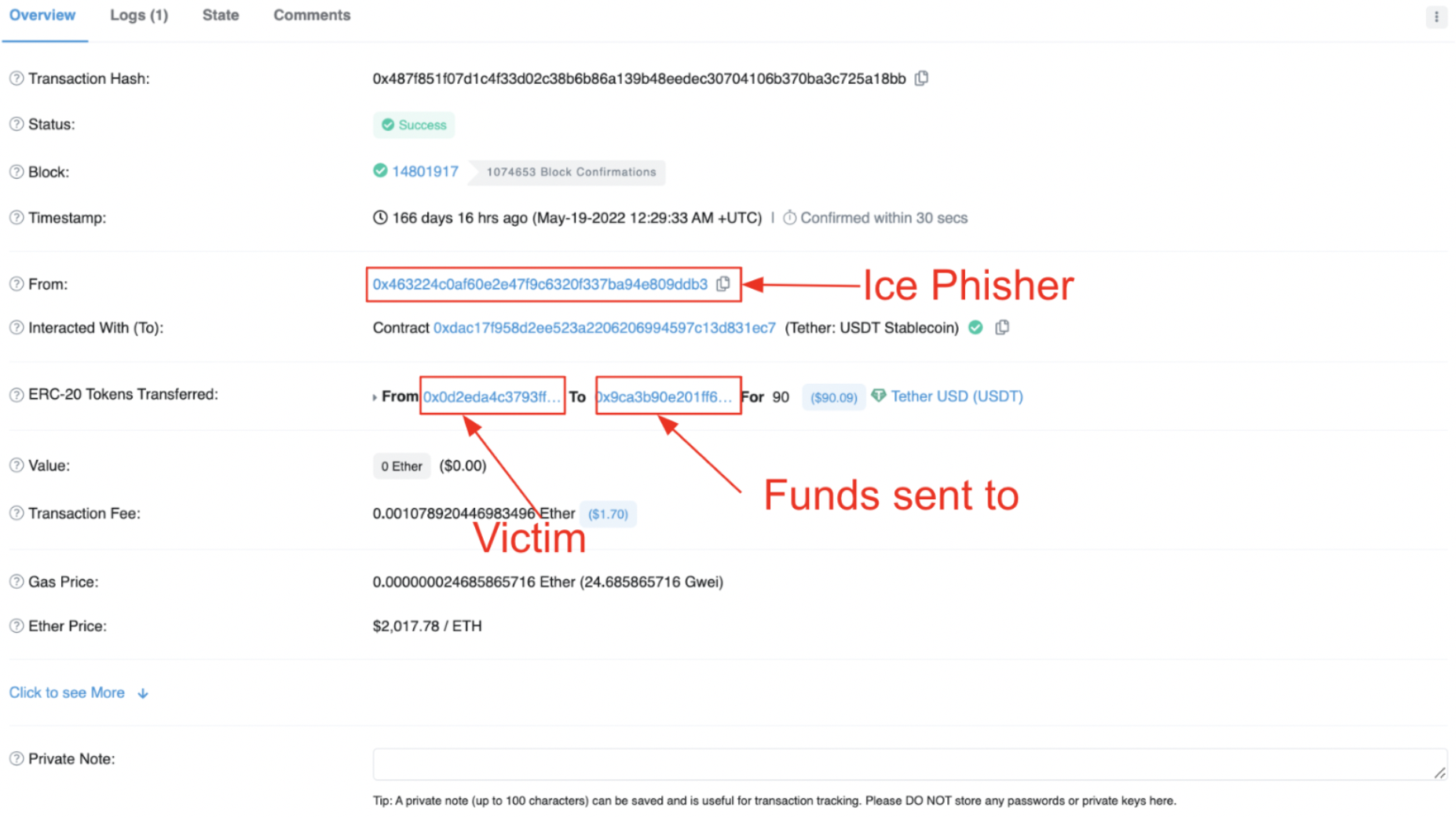
In this scenario, we observe that the ice phisher, represented by the address 0x4632, initializes the transaction involving the victim and the recipient. It's crucial to highlight that the recipient address may not necessarily belong to the wallet that conducted the ice phishing; rather, it's the wallet that triggered this specific transaction. Frequently, ice phishers redirect users' funds to a secondary Externally Owned Account (EOA) under their control. A visual representation of this transaction flow is depicted below:
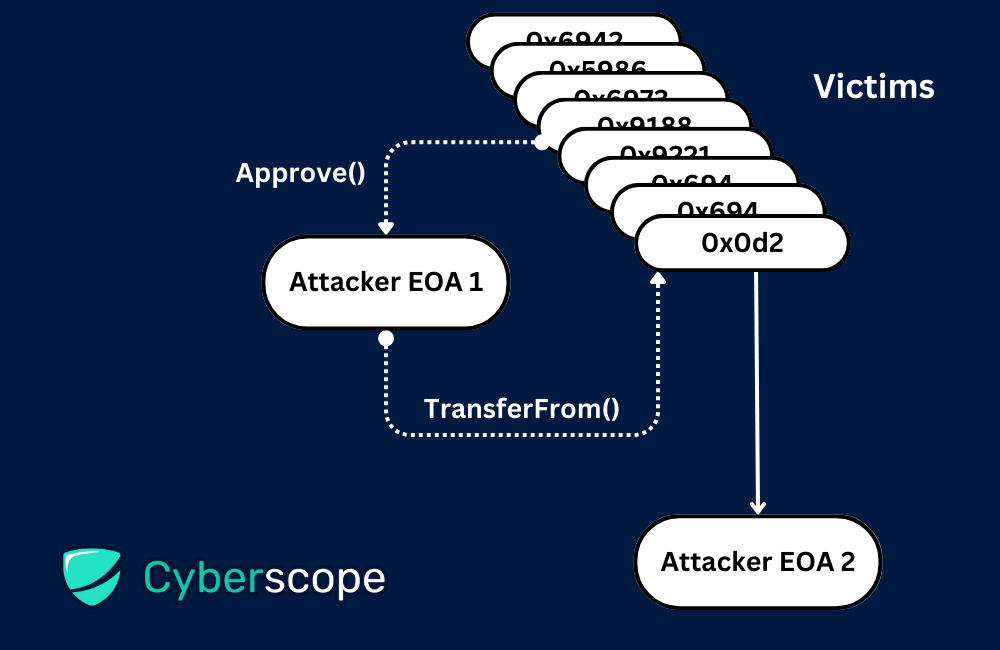
If you come across a transaction in your wallet that appears suspicious, it's essential to verify whether the initiating Externally Owned Account (EOA) has been granted the necessary permissions to utilize your tokens. You can easily perform this verification yourself by visiting scanning platforms like Etherscan.
If you see an address that you don’t recognize or one that has initiated transactions without your approval then you should revoke permissions. You can do this by visiting sites like revoke.cash or connecting your wallet to the scan site to revoke.
Here is how you revoke permissions on scan sites such as BscScan:
Visit https://bscscan.com/tokenapprovalchecker and search for your wallet
BscScan Token Approval Checker Connect your wallet
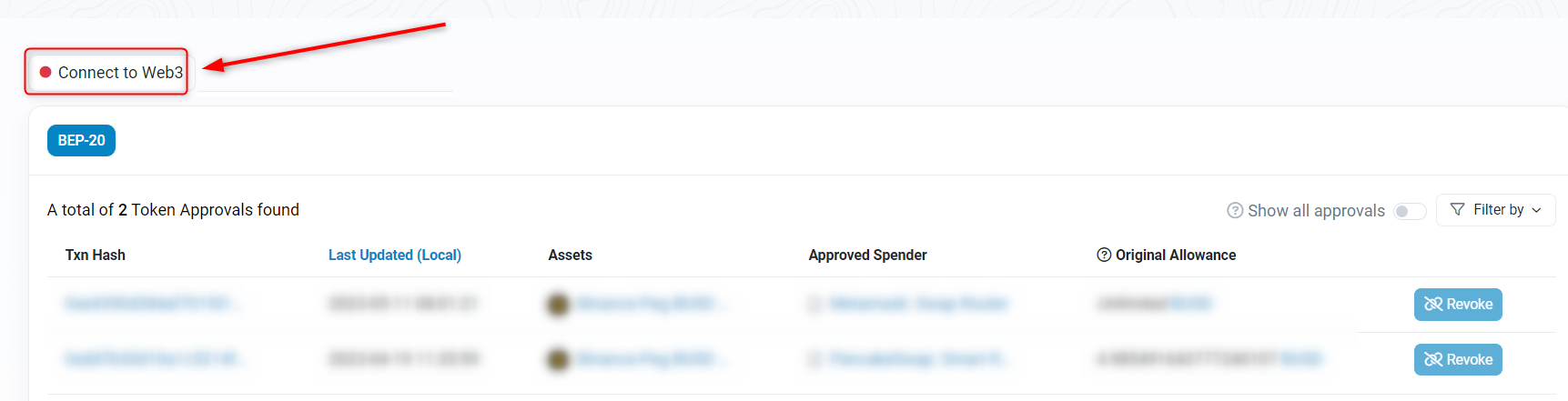
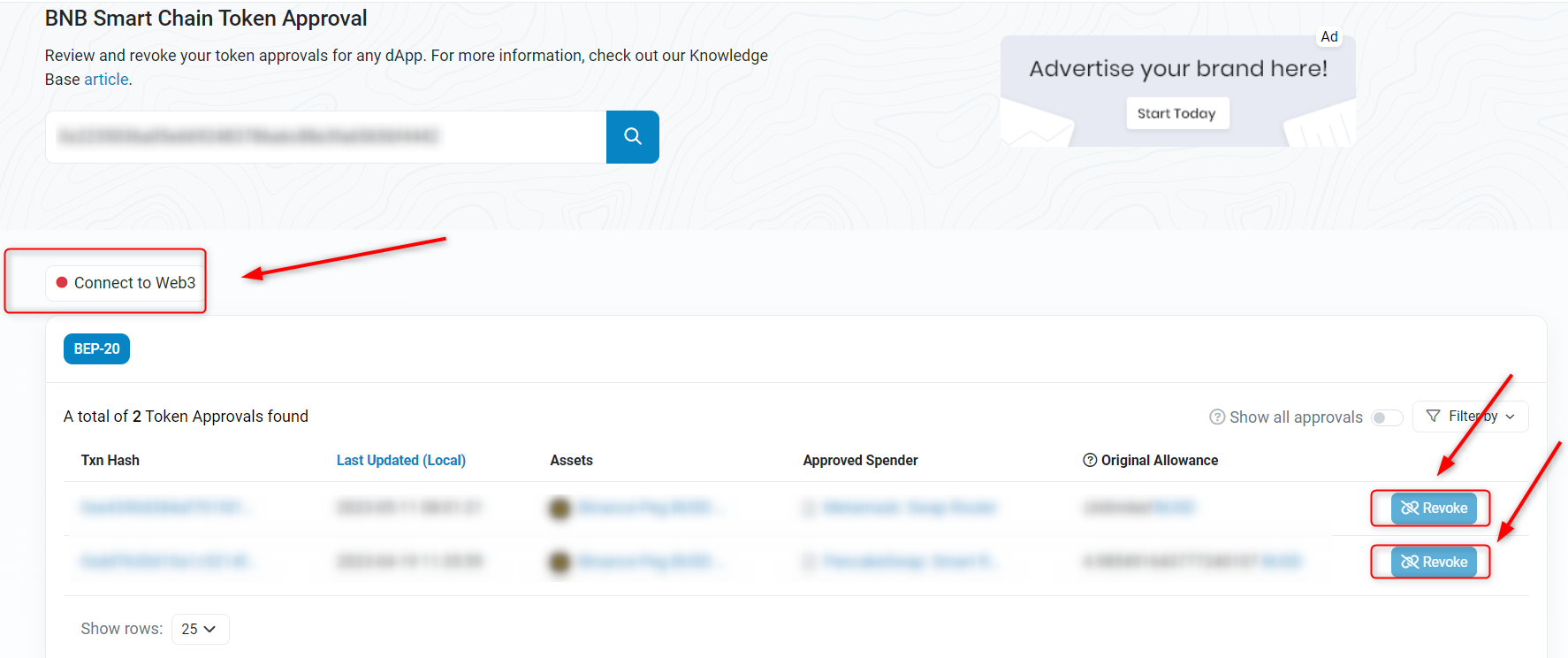
BscScan wallet connect - Hit the BEP-20 tab and find the address you wish to revoke.
- Click the Revoke button
Protecting Yourself from Ice Phishing
Now that we understand the modus operandi of ice phishing attacks, let's explore crucial steps to protect yourself from falling victim:
- Use Confirmed URLs: When accessing dApps or blockchain services, ensure you are using confirmed and verified URLs to avoid falling prey to phishing attempts or domain squatters.
- Double-check Transaction Details: Before approving any transaction, meticulously review the details, especially the recipient's address. Be cautious if anything seems amiss.
- Smart Contract Auditing: Consider opting for smart contract auditing services to assess the security and correctness of smart contracts you interact with. Audited contracts are generally safer.
- Transaction Verification: When signing transactions using wallets like Metamask, carefully scrutinize the transaction details to confirm that they align with your intentions.
- Cold Storage: For long-term holdings, like valuable NFTs or substantial cryptocurrency assets, consider storing them in cold storage wallets. Use hot wallets with a minimal balance for day-to-day transactions and dApp interactions.
- Monitor Smart Contracts: Check if the smart contracts you interact with have incident response mechanisms, such as pause/unpause functions. These can provide better control and security.
- Verify Contract Hash: When sending payments or granting access to crypto assets, verify the contract hash using blockchain explorers like Etherscan to ensure it's the correct entity.
- Authentic Communication: Always interact with official representatives of blockchain projects. Be cautious of individuals claiming to be customer support on social media platforms or Discord. Verify their authenticity through recognized email and official social media channels.
Conclusion
Ice phishing attacks represent a growing threat in the world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. By understanding the tactics employed by attackers and adopting vigilant security practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these scams. Safeguarding your digital assets in the web3 era requires not only the empowerment that decentralized systems offer but also a keen eye for security.
In an environment where the promise of financial freedom and autonomy abounds, staying informed and cautious is your best defence against the hidden dangers of ice phishing attacks.

.png%3Falt%3Dmedia&w=640&q=75)

